How Inflation Affects the Seattle Housing Market
September 8, 2023
Inflation and the housing market are interconnected, with changes in one affecting the other. Inflation can impact the housing market through interest rates, purchasing power, construction costs, rental prices, and investor behavior. These connections highlight the complex relationship between economic factors and the real estate market.
The Relationship Between Housing Inflation and Overall Inflation
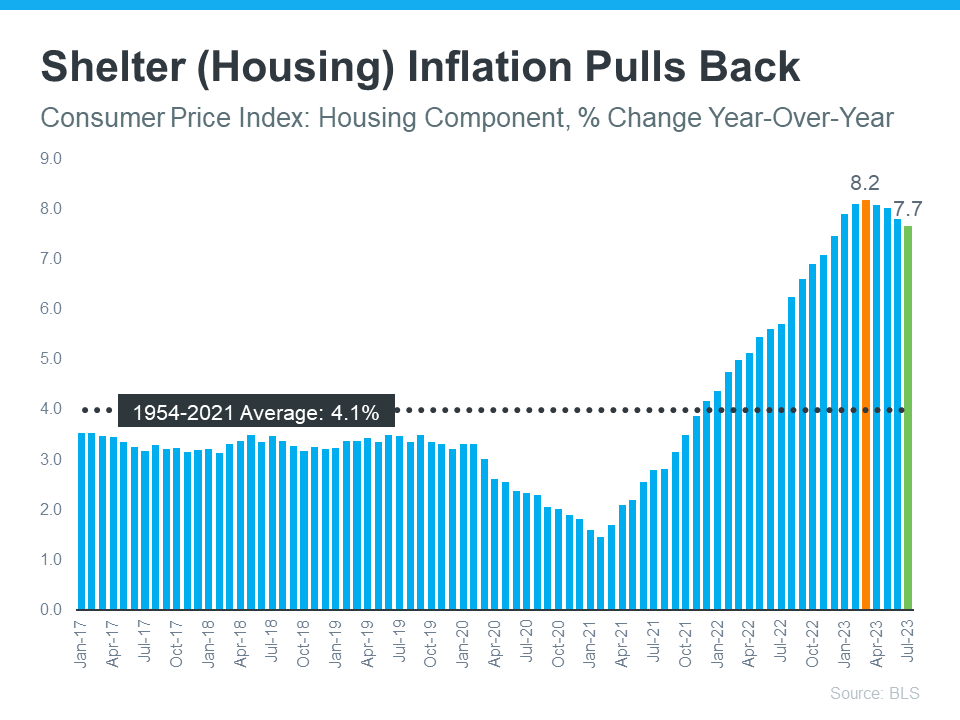
Shelter inflation is a housing-related measure of price growth, determined by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) through surveys of renters and homeowners. Renters report their monthly rent costs, while homeowners estimate what they would charge if they rented out their homes. This data helps gauge changes in housing costs over time.
Shelter inflation, which assesses housing costs, has been consistently decreasing for four consecutive months, similar to how overall inflation measures the cost of everyday items. This indicates a trend of reduced housing expenses (see graph below):
Why does this matter?
Shelter inflation, which accounts for about one-third of overall inflation as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), plays a significant role in determining overall inflation trends. The recent decline in shelter inflation could signal a potential decrease in overall inflation in the coming months.
This would be positive news for the Federal Reserve, as they have been working to manage and reduce inflation levels, aiming to reach their 2% target after it peaked at 8.9% in the middle of the previous year, with the latest report indicating it at 3.3%.
Inflation and the Federal Funds Rate
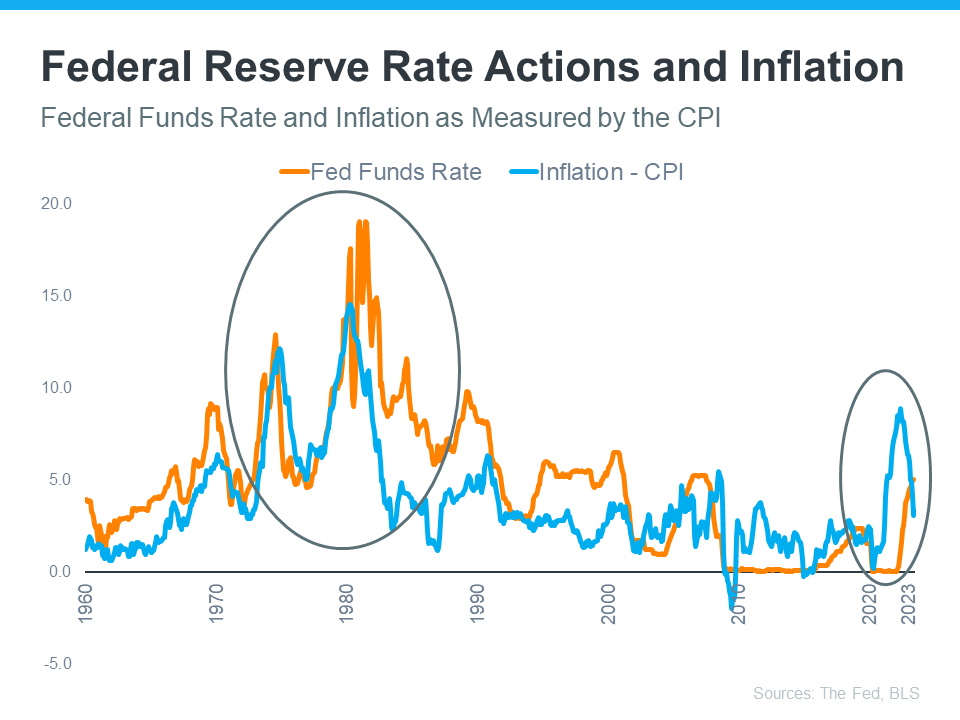
The Federal Reserve has been combatting inflation by raising the Federal Funds Rate, which affects the cost of interbank borrowing. As inflation increased, the Fed responded by increasing this rate to prevent the economy from overheating.
A clear relationship is shown in a graph, with inflation (blue line) rising triggering the Fed to raise the Federal Funds Rate (orange line) in an effort to bring inflation back down to their 2% target (see below):
In the graph, the circled section represents the recent spike in inflation, the Federal Reserve’s response to combat it by raising the Federal Funds Rate, and the subsequent moderation of inflation that resulted from this rate hike. As inflation approaches the Fed’s current 2% target, they may not need to increase the Federal Funds Rate significantly further, indicating a potential stabilization in their monetary policy.
A Brighter Future for Mortgage Rates?
So, what does all of this mean for you? While the actions coming out of the Fed don’t determine mortgage rates, they do have an impact. As Mortgage Professional America (MPA) explains:
“. . . mortgage rates and inflation are connected, however indirectly. When inflation rises, mortgage rates rise to keep up with the value of the US dollar. When inflation drops, mortgage rates follow suit.”
While no one can predict the future for mortgage rates, it’s encouraging to see the signs of moderating inflation in the economy.
Bottom Line
If you’re interested in the housing market, whether it’s for buying, selling, or staying informed, feel free to get in touch with us.